Inflation Definition- According to IMF, Inflation is the rate of increase in prices over a given period. Inflation is typically a broad measure, such as the overall increase in prices or the increase in the cost of living in a country.
Inflation is an increase in the prices of goods and services. The most well-known indicator of inflation is the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures the percentage change in the price of a basket of goods and services consumed by households.
Also Read: IMF Report
Types of Inflation:–
1. Demand-pull inflation.
2. Cost-push inflation.
3. Built-in inflation.
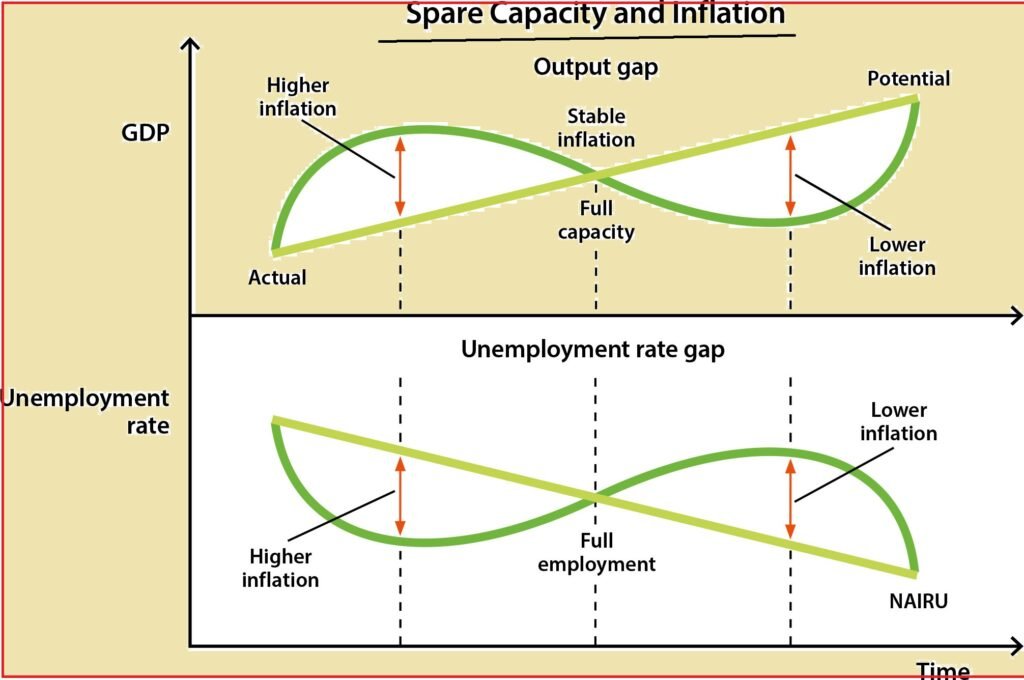
Demand-pull inflation:
Demand-pull inflation emerges when the all-out interest for labor and products (for example ‘total interest’) increments to surpass the stockpile of labor and products (for example ‘total stock’) that can be economically created.
The overabundance request comes down on costs across a wide scope of labor and products and at last, prompts an expansion in expansion – that is, it ‘pulls’ expansion higher.
Cost-push inflation:
Cost-push inflation happens when the absolute stockpile of labor and products in the economy which can be created (total stock) falls. A fall in total stock is much of the time brought about by an expansion in the expense of creation. Assuming total stock falls however total interest stays unaltered, there is up tension on costs and expansion – that is, expansion is ‘pushed’ higher.
Conversion scale developments can likewise influence costs and impact expansion results. A reduction in the worth of the homegrown money − that is, a deterioration − will increment expansion in two ways. In the first place, the costs of labor and products delivered abroad are ascent compared with those created locally.
What’s causing inflation in 2022?
Store network stresses expanded costs for products and transportation, which are cost inputs for completed merchandise. In nations where food comprised an enormous piece of the expansion increment, rising costs constrained low-pay buyers to lessen spending on different merchandise, in this way easing back financial development.
Why is inflation bad for the economy?
Inflation is measured by the consumer price index (CPI), also, at low rates, it keeps the economy sound. Yet, when the pace of expansion rises quickly, it can bring about lower buying power, higher loan fees, more slow monetary development, and other negative financial impacts.
What is the highest inflation rate ever?
The inflation Rate in the United States averaged 3.29 percent from 1914 until 2022, reaching an all-time high of 23.70 percent in June of 1920 and a record low of -15.80 percent in June of 1921.
What causes inflation in America?
If we take an example for better understanding, expanding unrefined substances or work expenses could compel organizations to raise the costs of the labor and products they sell. On the off chance that enough organizations are impacted and raise their costs, it can prompt a general expansion in costs and higher expansion rates.
How to stop inflation?
One of the fundamental instruments The Fed uses to fix expansion is raising loan costs. This is an illustration of financial arrangement. The public authority can acquaint financial strategies with decreased expansion by expanding charges or cutting spending.
Read Also: Cloud Market Share in 2022-2023


Leave a comment